LLM Observability with LangFuse, OpenRouter, and Encore.ts
Building AI apps with built-in observability. Track every call, optimize performance.

Building production LLM applications requires understanding what's actually happening with your AI calls: which prompts are being used, how many tokens each request consumes, what everything costs, and how long requests take. Without this visibility, it's difficult to optimize performance, control costs, or debug issues when users report problems.
LangFuse is an open-source observability platform specifically designed for LLM applications. It captures detailed traces of every AI interaction, including prompts, completions, token usage, costs, and latency. Combined with OpenRouter, which provides a unified API for accessing models from OpenAI, Anthropic, Meta, and other providers, you get both the data to optimize and the flexibility to experiment with different models.
In this tutorial, we'll build and deploy a chat backend with full observability. You'll learn how to instrument LLM calls, track costs across different models, collect user feedback, and use the resulting data to make informed optimization decisions.
Why LangFuse + OpenRouter?
LangFuse gives you visibility into your LLM calls:
- See every prompt and completion
- Track token usage and costs
- Measure latency and performance
- Collect user feedback
- Build evaluation datasets
OpenRouter gives you access to multiple LLM providers through one API:
- Claude 4.5 Opus, GPT-5, Gemini 3 Pro, Llama 3.3, and more
- Pay-as-you-go pricing
- Automatic fallbacks
- Model routing based on performance
Together, they let you experiment with different models and track which ones work best for your use case.
What we're building
We'll build a complete chat application with full LLM observability:
- Chat API - Completions via OpenRouter with multiple model support
- Request tracing - Every LLM call logged to LangFuse with full context
- Cost analysis - Track spending per model, user, and query
- Performance monitoring - Latency and token usage metrics
- Chat history - Auto-provisioned PostgreSQL database with session management
- User feedback - Rate responses and track quality scores
- Model comparison - Run the same prompt through different models
- Chat interface - Clean, minimal UI with conversation history
By the end, you'll have complete visibility into your LLM usage and the data to optimize.

Getting started
encore app create --example=ts/langfuse-openrouter to start with a complete working example. This tutorial walks through building it from scratch to understand each component.First, install Encore if you haven't already:
# macOS
brew install encoredev/tap/encore
# Linux
curl -L https://encore.dev/install.sh | bash
# Windows
iwr https://encore.dev/install.ps1 | iex
Create a new Encore application. This will prompt you to create a free Encore account if you don't have one (required for secret management):
encore app create langfuse-app --example=ts/hello-world
cd langfuse-app
Setting up LangFuse
Creating your LangFuse account
- Go to cloud.langfuse.com and sign up for a free account
- Create a new project
- Navigate to Settings and copy your API keys (public and secret)
Alternatively, you can self-host LangFuse using Docker.
Setting up OpenRouter
- Go to openrouter.ai and sign up
- Navigate to Keys and create an API key
- Copy your API key
- (Optional) Add credits to your account for production use
OpenRouter gives you access to Claude 4.5 Opus, GPT-5, Gemini 3 Pro, Llama 3.3, and dozens of other models through a single API.
Installing dependencies
Install LangFuse and OpenAI SDK (OpenRouter is OpenAI-compatible):
npm install langfuse openai
Backend implementation
Creating the AI service
Every Encore service starts with a service definition file (encore.service.ts). Services let you divide your application into logical components. At deploy time, you can decide whether to colocate them in a single process or deploy them as separate microservices, without changing a single line of code:
// ai/encore.service.ts
import { Service } from "encore.dev/service";
export default new Service("ai");
Configuring LangFuse and OpenRouter
Store your API keys securely using Encore's built-in secrets management:
// ai/clients.ts
import { Langfuse } from "langfuse";
import OpenAI from "openai";
import { secret } from "encore.dev/config";
const langfuseSecretKey = secret("LangfuseSecretKey");
const langfusePublicKey = secret("LangfusePublicKey");
const openrouterKey = secret("OpenRouterKey");
export const langfuse = new Langfuse({
secretKey: langfuseSecretKey(),
publicKey: langfusePublicKey(),
baseUrl: "https://cloud.langfuse.com",
});
export const openrouter = new OpenAI({
baseURL: "https://openrouter.ai/api/v1",
apiKey: openrouterKey(),
});
Set your API keys for local development:
# LangFuse keys
encore secret set --dev LangfuseSecretKey
encore secret set --dev LangfusePublicKey
# OpenRouter key
encore secret set --dev OpenRouterKey
# For production
encore secret set --prod LangfuseSecretKey
encore secret set --prod LangfusePublicKey
encore secret set --prod OpenRouterKey
Setting up the database
To store chat history and track conversations, create a PostgreSQL database. With Encore, you can create a database by simply defining it in code. The framework automatically provisions the infrastructure locally using Docker.
Create the database instance:
// ai/db.ts
import { SQLDatabase } from "encore.dev/storage/sqldb";
export const db = new SQLDatabase("ai", {
migrations: "./migrations",
});
Create the migration file:
-- ai/migrations/1_create_chat_history.up.sql
CREATE TABLE chat_messages (
id TEXT PRIMARY KEY,
user_id TEXT,
session_id TEXT NOT NULL,
role TEXT NOT NULL,
content TEXT NOT NULL,
model TEXT NOT NULL,
langfuse_trace_id TEXT,
tokens_used INTEGER,
cost_usd DECIMAL(10, 6),
latency_ms INTEGER,
rating INTEGER,
created_at TIMESTAMP NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP
);
CREATE INDEX idx_messages_session ON chat_messages(session_id, created_at);
CREATE INDEX idx_messages_trace ON chat_messages(langfuse_trace_id);
CREATE INDEX idx_messages_user ON chat_messages(user_id, created_at DESC);
Adding observability to chat completions
The key is instrumenting your LLM calls with LangFuse. Here's a chat endpoint that tracks everything:
// ai/chat.ts
import { api } from "encore.dev/api";
import { langfuse, openrouter } from "./clients";
import { db } from "./db";
import log from "encore.dev/log";
interface ChatRequest {
message: string;
model?: string;
userId?: string;
sessionId?: string;
}
interface ChatResponse {
messageId: string;
response: string;
model: string;
traceId: string;
tokensUsed: number;
latencyMs: number;
costUsd: number;
}
export const chat = api(
{ expose: true, method: "POST", path: "/ai/chat" },
async (req: ChatRequest): Promise<ChatResponse> => {
const startTime = Date.now();
const model = req.model || "anthropic/claude-4.5-opus";
const sessionId = req.sessionId || `session-${Date.now()}`;
const messages = [
{
role: "user" as const,
content: req.message,
},
];
// Create a LangFuse trace for this chat completion
const trace = langfuse.trace({
name: "chat-completion",
userId: req.userId,
sessionId,
input: messages,
metadata: {
model,
},
tags: ["chat", model.split("/")[0]],
});
try {
// Create a generation span within the trace
const generation = trace.generation({
name: "openrouter-completion",
model,
modelParameters: {
max_tokens: 1000,
},
input: messages,
});
log.info("Starting chat completion", { traceId: trace.id, model });
// Call OpenRouter for completion
const completion = await openrouter.chat.completions.create({
model,
messages,
max_tokens: 1000,
});
const response = completion.choices[0]?.message?.content || "";
const tokensUsed = completion.usage?.total_tokens || 0;
const latency = Date.now() - startTime;
// Estimate cost (rates vary by model)
const costPer1kTokens = model.includes("claude-4.5-opus") ? 0.015 : 0.002;
const cost = (tokensUsed / 1000) * costPer1kTokens;
// Update the generation span with output and metadata
generation.end({
output: response,
usage: {
totalTokens: tokensUsed,
input: completion.usage?.prompt_tokens || 0,
output: completion.usage?.completion_tokens || 0,
},
metadata: {
latencyMs: latency,
costUsd: cost,
},
});
// Store user message
const userMessageId = `msg-${Date.now()}-${Math.random().toString(36).slice(2, 11)}`;
await db.exec`
INSERT INTO chat_messages (
id, user_id, session_id, role, content, model,
langfuse_trace_id, tokens_used, cost_usd, latency_ms
)
VALUES (
${userMessageId}, ${req.userId}, ${sessionId}, 'user', ${req.message}, ${model},
${trace.id}, 0, 0, 0
)
`;
// Store assistant response
const assistantMessageId = `msg-${Date.now()}-${Math.random().toString(36).slice(2, 11)}`;
await db.exec`
INSERT INTO chat_messages (
id, user_id, session_id, role, content, model,
langfuse_trace_id, tokens_used, cost_usd, latency_ms
)
VALUES (
${assistantMessageId}, ${req.userId}, ${sessionId}, 'assistant', ${response}, ${model},
${trace.id}, ${tokensUsed}, ${cost}, ${latency}
)
`;
log.info("Chat completion successful", {
messageId: assistantMessageId,
traceId: trace.id,
tokensUsed,
latencyMs: latency,
});
// Update trace with output
trace.update({
output: response,
});
// Finalize the trace
await langfuse.flushAsync();
return {
messageId: assistantMessageId,
response,
model,
traceId: trace.id,
tokensUsed,
latencyMs: latency,
costUsd: cost,
};
} catch (error) {
// Track errors in LangFuse
trace.event({
name: "completion-error",
metadata: {
error: error instanceof Error ? error.message : "Unknown error",
},
});
await langfuse.flushAsync();
throw error;
}
}
);
What's being tracked:
- Input: The user's message and selected model
- Output: The LLM's complete response
- Tokens: Prompt tokens, completion tokens, total
- Cost: Estimated based on model pricing
- Latency: Time from request to response
- Metadata: User ID, session ID, model used
LangFuse now has a complete record of this request. You can see it in the dashboard, filter by user or model, and analyze patterns.
Listing chat history
Create an endpoint to retrieve chat history for a session:
// ai/chat.ts (continued)
interface ChatMessage {
id: string;
role: string;
content: string;
model: string;
tokensUsed: number;
costUsd: number;
createdAt: Date;
traceId: string | null;
rating: number | null;
}
interface ChatHistoryRequest {
sessionId: string;
}
interface ChatHistoryResponse {
messages: ChatMessage[];
totalTokens: number;
totalCost: number;
}
export const getChatHistory = api(
{ expose: true, method: "GET", path: "/ai/chat/:sessionId" },
async ({ sessionId }: ChatHistoryRequest): Promise<ChatHistoryResponse> => {
const rows = await db.query<{
id: string;
role: string;
content: string;
model: string;
tokens_used: number;
cost_usd: number;
created_at: Date;
langfuse_trace_id: string | null;
rating: number | null;
}>`
SELECT id, role, content, model, tokens_used, cost_usd, created_at, langfuse_trace_id, rating
FROM chat_messages
WHERE session_id = ${sessionId}
ORDER BY created_at ASC
`;
const messages: ChatMessage[] = [];
let totalTokens = 0;
let totalCost = 0;
for await (const row of rows) {
messages.push({
id: row.id,
role: row.role,
content: row.content,
model: row.model,
tokensUsed: row.tokens_used,
costUsd: row.cost_usd,
createdAt: row.created_at,
traceId: row.langfuse_trace_id,
rating: row.rating,
});
totalTokens += row.tokens_used;
totalCost += Number(row.cost_usd);
}
return { messages, totalTokens, totalCost };
}
);
Adding user feedback
LangFuse supports user feedback scores. Create an endpoint to rate chat responses:
// ai/feedback.ts
import { api } from "encore.dev/api";
import { langfuse } from "./clients";
import { db } from "./db";
interface AddFeedbackRequest {
traceId: string;
score: number; // 1-5
comment?: string;
}
interface AddFeedbackResponse {
success: boolean;
}
export const addFeedback = api(
{ expose: true, method: "POST", path: "/ai/feedback" },
async (req: AddFeedbackRequest): Promise<AddFeedbackResponse> => {
// Send to LangFuse
await langfuse.score({
traceId: req.traceId,
name: "user-rating",
value: req.score,
comment: req.comment,
});
await langfuse.flushAsync();
// Also store in database
await db.exec`
UPDATE chat_messages
SET rating = ${req.score}
WHERE langfuse_trace_id = ${req.traceId}
AND role = 'assistant'
`;
return { success: true };
}
);
Tracking costs
Add cost tracking across different models:
// ai/costs.ts
import { api } from "encore.dev/api";
import { db } from "./db";
interface CostSummaryResponse {
totalCost: number;
totalTokens: number;
costsByModel: Record<string, { cost: number; tokens: number; messages: number }>;
}
export const getCostSummary = api(
{ expose: true, method: "GET", path: "/ai/costs" },
async (): Promise<CostSummaryResponse> => {
const rows = await db.query<{
model: string;
total_cost: number;
total_tokens: number;
message_count: number;
}>`
SELECT
model,
SUM(cost_usd) as total_cost,
SUM(tokens_used) as total_tokens,
COUNT(*) as message_count
FROM chat_messages
WHERE role = 'assistant'
GROUP BY model
`;
const costsByModel: Record<string, { cost: number; tokens: number; messages: number }> = {};
let totalCost = 0;
let totalTokens = 0;
for await (const row of rows) {
costsByModel[row.model] = {
cost: Number(row.total_cost),
tokens: row.total_tokens,
messages: row.message_count,
};
totalCost += Number(row.total_cost);
totalTokens += row.total_tokens;
}
return {
totalCost,
totalTokens,
costsByModel,
};
}
);
Testing locally
Start your backend (make sure Docker is running first):
encore run
Your API is now running locally. Open the local development dashboard at http://localhost:9400 to explore your API.

Send a chat message
curl -X POST http://localhost:4000/ai/chat \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"message": "Explain quantum computing in simple terms",
"model": "anthropic/claude-4.5-opus",
"userId": "user123",
"sessionId": "session456"
}'
Response:
{
"messageId": "msg-1234567890-abc",
"response": "Quantum computing is a revolutionary approach to processing information...",
"model": "anthropic/claude-4.5-opus",
"traceId": "trace_xyz123",
"tokensUsed": 245,
"latencyMs": 1850,
"costUsd": 0.003675
}
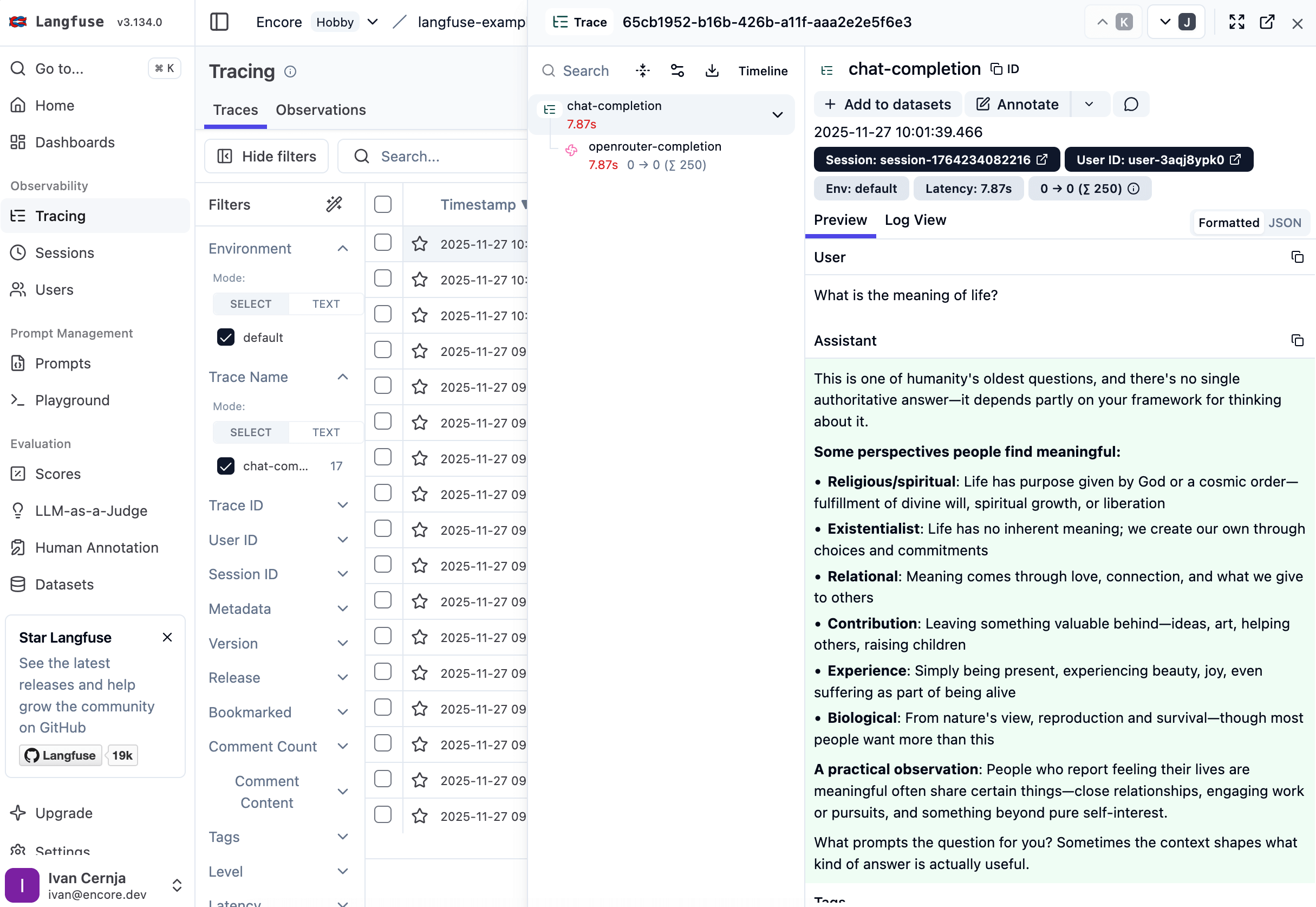
View the trace in LangFuse
Open cloud.langfuse.com and navigate to Traces. Find your trace and you'll see:
- Complete prompt and response - The exact input and output
- Token breakdown - How many tokens for prompt vs completion
- Cost calculation - Exact spend for this request
- Timing - How long the LLM took to respond
- Model details - Which model handled the request
This is the power of observability. Instead of guessing, you know exactly what happened.
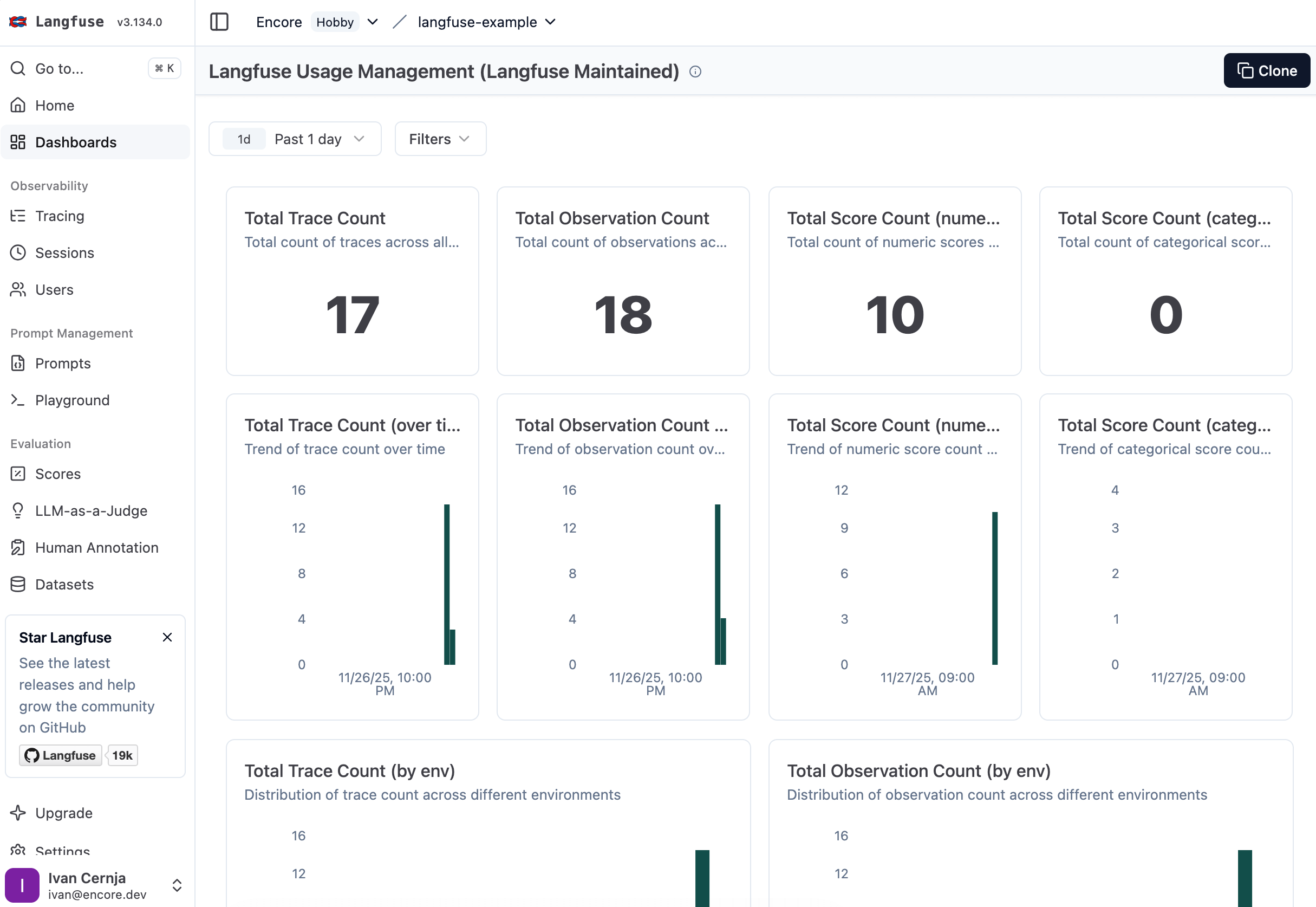
Compare models with real data
Now let's see how different models perform for the same task:
# Claude 4.5 Opus (highest quality, premium cost)
curl -X POST http://localhost:4000/ai/chat \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"message":"What is TypeScript?","model":"anthropic/claude-4.5-opus"}'
# GPT-5 (high quality, high cost)
curl -X POST http://localhost:4000/ai/chat \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"message":"What is TypeScript?","model":"openai/gpt-5"}'
# Llama 3.3 70B (good quality, low cost)
curl -X POST http://localhost:4000/ai/chat \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"message":"What is TypeScript?","model":"meta-llama/llama-3.3-70b-instruct"}'
In LangFuse, you can now compare these side-by-side:
- Claude 4.5 Opus took 2.1s and cost $0.0037
- GPT-5 took 2.5s and cost $0.0028
- Llama 3.3 took 0.8s and cost $0.0002
For simple questions, Llama might be perfect. For complex reasoning, Claude 4.5 Opus or GPT-5. You have the data to decide.
Add feedback
curl -X POST http://localhost:4000/ai/feedback \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"traceId": "trace_xyz123",
"score": 5,
"comment": "Great explanation!"
}'
Get chat history
curl http://localhost:4000/ai/chat/session456
Check costs
curl http://localhost:4000/ai/costs
Exploring the local dashboard
The local development dashboard at http://localhost:9400 provides:
- API Explorer - Test all your endpoints interactively
- Service Catalog - Auto-generated API documentation
- Architecture Diagram - Visual representation of your services
- Distributed Tracing - See the full flow including OpenRouter and LangFuse API calls
- Database Explorer - Browse your chat messages, costs, and traces
Combined with LangFuse's dashboard, you get complete visibility into both your application flow and your LLM calls.
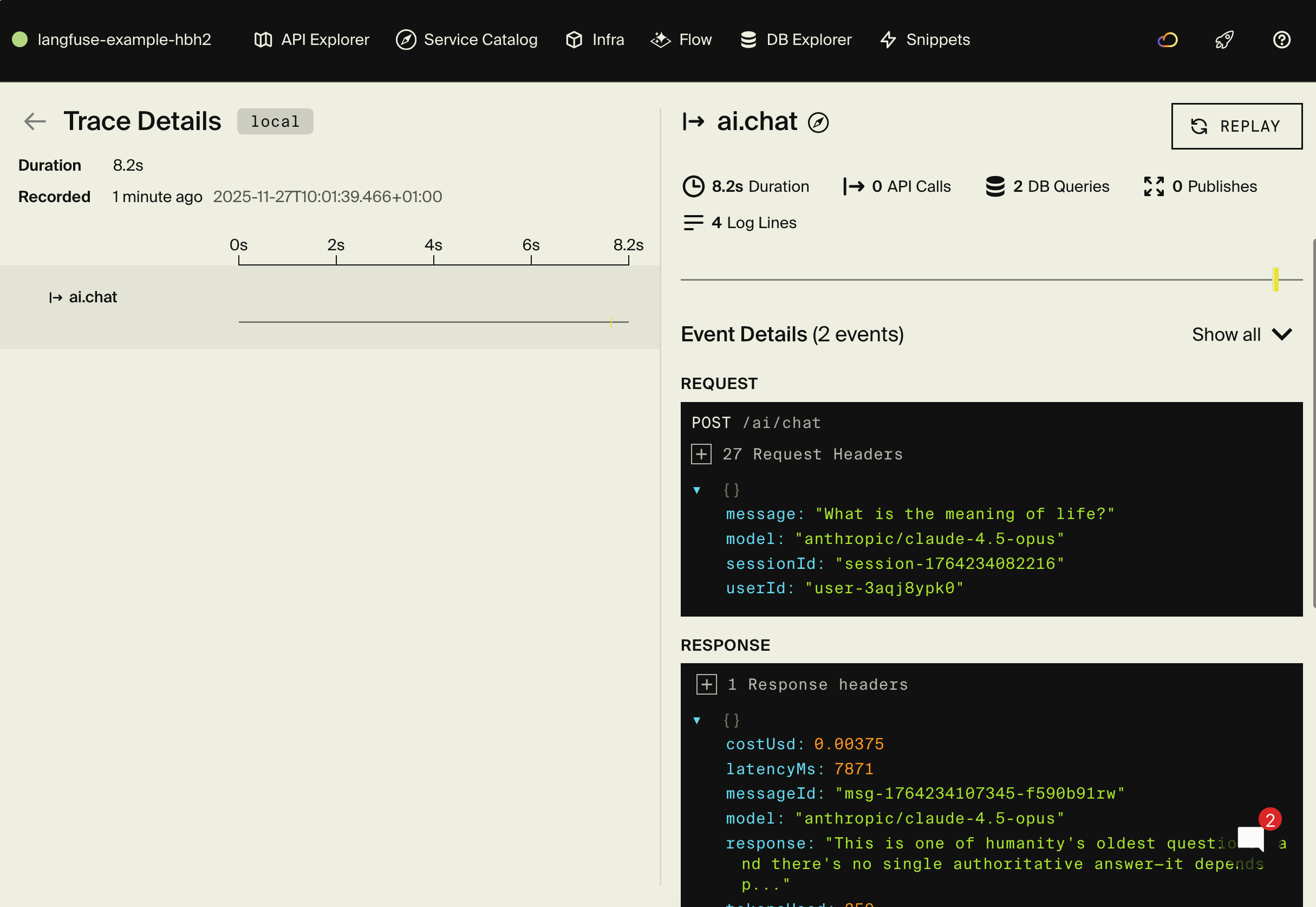
Advanced features
Prompt versioning
Track different versions of your prompts to compare effectiveness:
const trace = langfuse.trace({
name: "chat-completion",
metadata: {
promptVersion: "v2",
systemPrompt: "You are a helpful assistant specialized in {topic}",
},
});
Model comparison
Compare different models for the same task:
export const compareModels = api(
{ expose: true, method: "POST", path: "/ai/compare" },
async (req: { message: string; models: string[] }) => {
const trace = langfuse.trace({
name: "model-comparison",
metadata: { models: req.models },
});
const results = [];
for (const model of req.models) {
const messages = [{ role: "user" as const, content: req.message }];
const generation = trace.generation({
name: `openrouter-${model}`,
model,
input: messages,
});
const completion = await openrouter.chat.completions.create({
model,
messages,
});
const response = completion.choices[0]?.message?.content || "";
const tokensUsed = completion.usage?.total_tokens || 0;
generation.end({
output: response,
usage: { totalTokens: tokensUsed },
});
results.push({
model,
response,
tokensUsed,
});
}
await langfuse.flushAsync();
return { results, traceId: trace.id };
}
);
Custom metrics
Add custom metrics to track specific aspects of your LLM responses:
trace.event({
name: "response-analysis",
metadata: {
responseLength: response.length,
containsCode: response.includes("```"),
sentiment: "positive",
language: "en",
},
});
A/B testing
Compare different models or system prompts:
const variant = Math.random() < 0.5 ? "A" : "B";
const model = variant === "A"
? "anthropic/claude-4.5-opus"
: "openai/gpt-5";
const trace = langfuse.trace({
name: "chat-completion",
metadata: {
experiment: "model-comparison-2025",
variant,
model,
},
});
Using the data
Once you have traces flowing into LangFuse, you can use the dashboard to identify optimization opportunities:
Cost analysis - Group traces by model to see total spend. If GPT-5 and Claude 4.5 Opus have similar user ratings but different costs, switch to the cheaper one. Filter by user to find high-volume users consuming a disproportionate share of your budget.
Latency tracking - Sort traces by duration to find slow queries. Cross-reference with the prompts and models used. The 95th percentile latency matters more than the average - that's what users actually experience during peak times.
Quality metrics - User ratings tell you which responses work. After changing a prompt template, compare before/after ratings to validate the improvement. Sort by lowest ratings to find queries that need work.
Token optimization - Traces show exact token counts per request. Identify queries using excessive tokens and refine the prompts. Small changes can significantly reduce costs at scale.
Adding a chat interface
For quick demos and prototypes, you can serve a static HTML frontend directly from your Encore app using api.static():
// frontend/static.ts
import { api } from "encore.dev/api";
export const assets = api.static(
{ expose: true, path: "/!path", dir: "./" }
);
// frontend/encore.service.ts
import { Service } from "encore.dev/service";
export default new Service("frontend");
The path: "/!path" pattern serves as a fallback route, meaning it will match any path that doesn't match your API endpoints. This works great for single-page applications.
Create a minimal chat interface in frontend/index.html:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>AI Chat</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="styles.css">
</head>
<body>
<div class="app">
<aside class="sidebar">
<button class="new-chat-btn" onclick="createNewChat()">+ New Chat</button>
<div class="chat-history" id="chat-history"></div>
</aside>
<main class="main">
<header class="chat-header">
<h1>AI Chat</h1>
<div class="stats">
<span><span id="total-cost">$0.00</span></span>
<span><span id="total-tokens">0</span> tokens</span>
</div>
</header>
<div class="messages" id="messages"></div>
<div class="input-container">
<textarea id="message-input" placeholder="Type your message..."></textarea>
<button id="send-btn" onclick="sendMessage()">Send</button>
</div>
</main>
</div>
<script src="app.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
The JavaScript handles API calls, session management, and chat history:
// frontend/app.js
const API_BASE = 'http://localhost:4000';
let currentSessionId = null;
let sessions = JSON.parse(localStorage.getItem('chat_sessions') || '[]');
async function sendMessage() {
const input = document.getElementById('message-input');
const message = input.value.trim();
if (!message) return;
const response = await fetch(`${API_BASE}/ai/chat`, {
method: 'POST',
headers: { 'Content-Type': 'application/json' },
body: JSON.stringify({
message,
model: 'anthropic/claude-4.5-opus',
userId: 'user123',
sessionId: currentSessionId
})
});
const data = await response.json();
addMessage('assistant', data.response, data.model, {
tokens: data.tokensUsed,
cost: data.costUsd,
traceId: data.traceId
});
}
Static files are served directly from Encore's Rust runtime with zero JavaScript execution, making them extremely fast. When you deploy with git push encore, your frontend deploys alongside your backend, giving you a single URL you can immediately share to demo your prototype.
For production applications with more complex frontend needs (React, Next.js, build pipelines), we recommend deploying your frontend to Vercel, Netlify, or similar services and using the generated API client to call your Encore backend.
Please note
Full example code: The complete chat interface with session management, chat history sidebar, rating persistence, and minimal Apple-like design is available in the example repository.
Deployment
Self-hosting
See the self-hosting instructions for how to use encore build docker to create a Docker image.
Encore Cloud Platform
Deploy your application using git push encore:
git add -A .
git commit -m "Add LangFuse observability"
git push encore
Set your production secrets:
encore secret set --prod LangfuseSecretKey
encore secret set --prod LangfusePublicKey
encore secret set --prod OpenRouterKey
Note: Encore Cloud is great for prototyping and development with fair use limits. For production workloads, you can connect your AWS or GCP account and Encore will provision infrastructure directly in your cloud account.
Next steps
- Set up LangFuse datasets for evaluation
- Configure LangFuse prompts for versioning
- Add custom evaluations for quality checks
- Implement LangFuse playground for prompt testing
- Set up cost tracking alerts
- Export data for custom analytics
If you found this tutorial helpful, consider starring Encore on GitHub to help others discover it.
More Articles


