Building an Uptime Monitor
Learn how to build an event-driven uptime monitoring system
Want to be notified when your website goes down so you can fix it before your users notice?
You need an uptime monitoring system. Sounds daunting? Don't worry, we'll build it with Encore in 30 minutes!
The app will use an event-driven architecture and the final result will look like this:
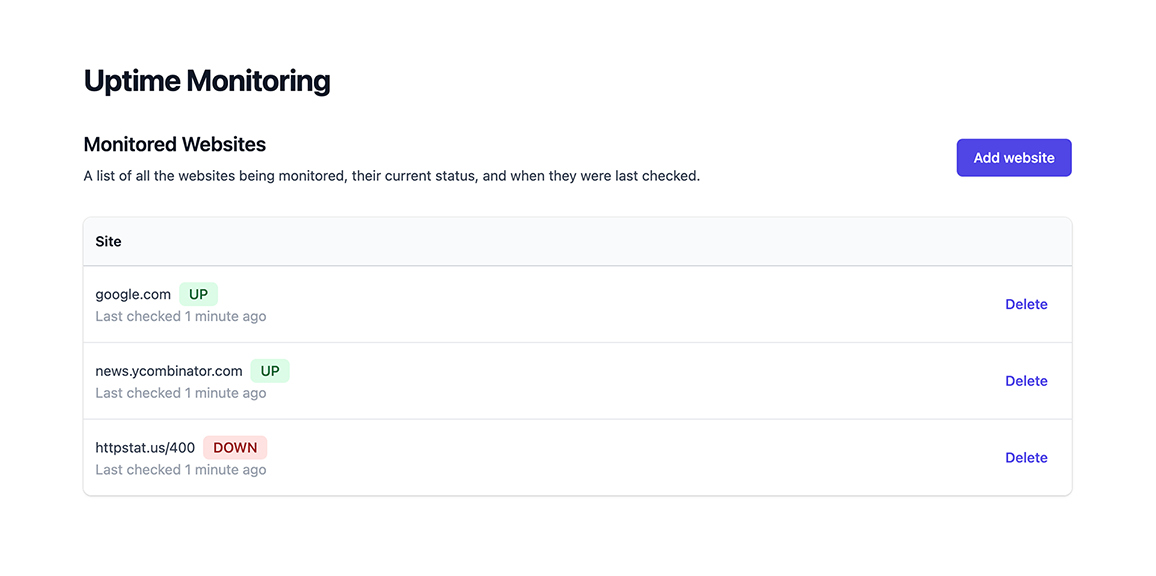
Project
1. Create your Encore application
Please note
To make it easier to follow along, we've laid out a trail of croissants to guide your way. Whenever you see a 🥐 it means there's something for you to do.
🥐 Create a new Encore application, using this tutorial project's starting-point branch. This gives you a ready-to-go frontend to use.
$ encore app create uptime --example=github.com/encoredev/example-app-uptime/tree/starting-pointIf this is the first time you're using Encore, you'll be asked if you wish to create a free account. This is needed when you want Encore to manage functionality like secrets and handle cloud deployments (which we'll use later on in the tutorial).
When we're done we'll have a backend with an event-driven architecture, as seen below in the automatically generated diagram where white boxes are services and black boxes are Pub/Sub topics:
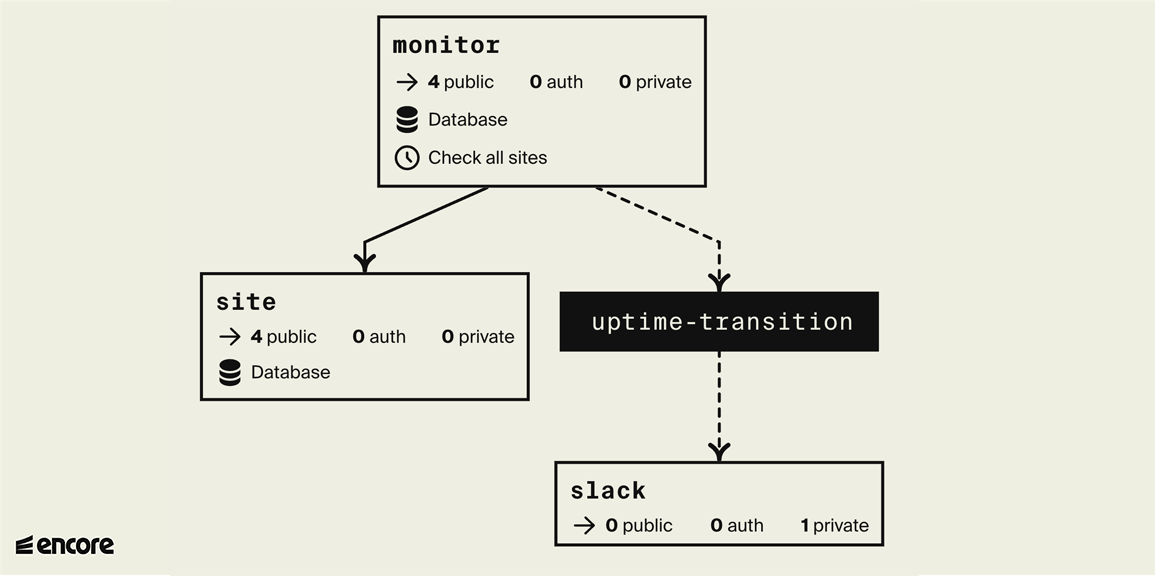
2. Create monitor service
Let's start by creating the functionality to check if a website is currently up or down. Later we'll store this result in a database so we can detect when the status changes and send alerts.
🥐 Create an Encore service named monitor containing a file named ping.go.
$ mkdir monitor$ touch monitor/ping.go🥐 Add an Encore API endpoint named Ping that takes a URL as input and returns a response
indicating whether the site is up or down.
monitor/ping.go// Service monitor checks if a website is up or down.
package monitor
import (
"context"
"net/http"
"strings"
)
// PingResponse is the response from the Ping endpoint.
type PingResponse struct {
Up bool `json:"up"`
}
// Ping pings a specific site and determines whether it's up or down right now.
//
//encore:api public path=/ping/*url
func Ping(ctx context.Context, url string) (*PingResponse, error) {
// If the url does not start with "http:" or "https:", default to "https:".
if !strings.HasPrefix(url, "http:") && !strings.HasPrefix(url, "https:") {
url = "https://" + url
}
// Make an HTTP request to check if it's up.
req, err := http.NewRequestWithContext(ctx, "GET", url, nil)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
resp, err := http.DefaultClient.Do(req)
if err != nil {
return &PingResponse{Up: false}, nil
}
resp.Body.Close()
// 2xx and 3xx status codes are considered up
up := resp.StatusCode < 400
return &PingResponse{Up: up}, nil
}
🥐 Let's try it! Run encore run in your terminal and you should see the service start up.
Then open up the Local Development Dashboard at http://localhost:9400 and try calling the monitor.ping endpoint from the API Explorer, passing in google.com as the URL.
You can then see the response, logs, and view a trace of the request. It will look something like this:
If you prefer to use the terminal instead run curl http://localhost:4000/ping/google.com in
a new terminal instead. Either way you should see the response:
{"up": true}
You can also try with httpstat.us/400 and some-non-existing-url.com and it should respond with {"up": false}.
(It's always a good idea to test the negative case as well.)
Add a test
🥐 Let's write an automated test so we don't break this endpoint over time. Create the file monitor/ping_test.go
with the content:
monitor/ping_test.gopackage monitor
import (
"context"
"testing"
)
func TestPing(t *testing.T) {
ctx := context.Background()
tests := []struct {
URL string
Up bool
}{
{"encore.dev", true},
{"google.com", true},
// Test both with and without "https://"
{"httpbin.org/status/200", true},
{"https://httpbin.org/status/200", true},
// 4xx and 5xx should considered down.
{"httpbin.org/status/400", false},
{"https://httpbin.org/status/500", false},
// Invalid URLs should be considered down.
{"invalid://scheme", false},
}
for _, test := range tests {
resp, err := Ping(ctx, test.URL)
if err != nil {
t.Errorf("url %s: unexpected error: %v", test.URL, err)
} else if resp.Up != test.Up {
t.Errorf("url %s: got up=%v, want %v", test.URL, resp.Up, test.Up)
}
}
}
🥐 Run encore test ./... to check that it all works as expected. You should see something like:
$ encore test ./...9:38AM INF starting request endpoint=Ping service=monitor test=TestPing9:38AM INF request completed code=ok duration=71.861792 endpoint=Ping http_code=200 service=monitor test=TestPing[... lots more lines ...]PASSok encore.app/monitor 1.660And if you open the local development dashboard at localhost:9400, you can also see traces for the tests.
3. Create site service
Next, we want to keep track of a list of websites to monitor.
Since most of these APIs will be simple "CRUD" (Create/Read/Update/Delete) endpoints, let's build this service using GORM, an ORM library that makes building CRUD endpoints really simple.
🥐 Let's create a new service named site with a SQL database. To do so, create a new directory site in the application root with migrations folder inside that folder:
$ mkdir site$ mkdir site/migrations🥐 Add a database migration file inside that folder, named 1_create_tables.up.sql.
The file name is important (it must look something like 1_<name>.up.sql).
Add the following contents:
site/migrations/1_create_tables.up.sqlCREATE TABLE sites (
id BIGSERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
url TEXT NOT NULL
);
🥐 Next, install the GORM library and PostgreSQL driver:
Now let's create the site service itself. To do this we'll use Encore's support for dependency injection to inject the GORM database connection.
🥐 Create site/service.go with the contents:
site/service.go// Service site keeps track of which sites to monitor.
package site
import (
"encore.dev/storage/sqldb"
"gorm.io/driver/postgres"
"gorm.io/gorm"
)
//encore:service
type Service struct {
db *gorm.DB
}
// Define a database named 'site', using the database migrations
// in the "./migrations" folder. Encore automatically provisions,
// migrates, and connects to the database.
var db = sqldb.NewDatabase("site", sqldb.DatabaseConfig{
Migrations: "./migrations",
})
// initService initializes the site service.
// It is automatically called by Encore on service startup.
func initService() (*Service, error) {
db, err := gorm.Open(postgres.New(postgres.Config{
Conn: db.Stdlib(),
}))
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
return &Service{db: db}, nil
}
🥐 With that, we're now ready to create our CRUD endpoints. Create the following files:
site/get.gosite/add.gosite/list.gosite/delete.gopackage site
import "context"
// Site describes a monitored site.
type Site struct {
// ID is a unique ID for the site.
ID int `json:"id"`
// URL is the site's URL.
URL string `json:"url"`
}
// Get gets a site by id.
//
//encore:api public method=GET path=/site/:siteID
func (s *Service) Get(ctx context.Context, siteID int) (*Site, error) {
var site Site
if err := s.db.Where("id = $1", siteID).First(&site).Error; err != nil {
return nil, err
}
return &site, nil
}
🥐 Now make sure you have Docker installed and running, and then restart encore run to cause the site database to be created by Encore.
You can verify that the database was created by looking at your application's Flow architecture diagram in the local development dashboard at localhost:9400, and then use the Service Catalog to call the site.Add endpoint.
Or you can call site.Add from the terminal:
$ curl -X POST 'http://localhost:4000/site' -d '{"url": "https://encore.dev"}'{ "id": 1, "url": "https://encore.dev"}4. Record uptime checks
In order to notify when a website goes down or comes back up, we need to track the previous state it was in.
🥐 To do so, let's add a database to the monitor service as well.
Create the directory monitor/migrations and the file monitor/migrations/1_create_tables.up.sql:
monitor/migrations/1_create_tables.up.sqlCREATE TABLE checks (
id BIGSERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
site_id BIGINT NOT NULL,
up BOOLEAN NOT NULL,
checked_at TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE NOT NULL
);
We'll insert a database row every time we check if a site is up.
🥐 Add a new endpoint Check to the monitor service, that
takes in a Site ID, pings the site, and inserts a database row
in the checks table.
For this service we'll use Encore's sqldb package
instead of GORM (in order to showcase both approaches).
monitor/check.gopackage monitor
import (
"context"
"encore.app/site"
"encore.dev/storage/sqldb"
)
// Check checks a single site.
//
//encore:api public method=POST path=/check/:siteID
func Check(ctx context.Context, siteID int) error {
site, err := site.Get(ctx, siteID)
if err != nil {
return err
}
result, err := Ping(ctx, site.URL)
if err != nil {
return err
}
_, err = db.Exec(ctx, `
INSERT INTO checks (site_id, up, checked_at)
VALUES ($1, $2, NOW())
`, site.ID, result.Up)
return err
}
// Define a database named 'monitor', using the database migrations
// in the "./migrations" folder. Encore automatically provisions,
// migrates, and connects to the database.
var db = sqldb.NewDatabase("monitor", sqldb.DatabaseConfig{
Migrations: "./migrations",
})
🥐 Restart encore run to cause the monitor database to be created.
We can again verify that the database was created in the Flow diagram, and also see the dependency between the monitor service and the site service that we just added.
We can then call the monitor.Check endpoint using the id 1 that we got in the last step, and view the trace where we see the database interactions.
It will look something like this:
🥐 You can also inspect the database using encore db shell <database-name> to make sure everything worked:
If that's what you see, everything's working great!
Add a cron job to check all sites
We now want to regularly check all the tracked sites so we can respond in case any of them go down.
We'll create a new CheckAll API endpoint in the monitor service
that will list all the tracked sites and check all of them.
🥐 Let's extract some of the functionality we wrote for the
Check endpoint into a separate function, like so:
monitor/check.go// Check checks a single site.
//
//encore:api public method=POST path=/check/:siteID
func Check(ctx context.Context, siteID int) error {
site, err := site.Get(ctx, siteID)
if err != nil {
return err
}
return check(ctx, site)
}
func check(ctx context.Context, site *site.Site) error {
result, err := Ping(ctx, site.URL)
if err != nil {
return err
}
_, err = db.Exec(ctx, `
INSERT INTO checks (site_id, up, checked_at)
VALUES ($1, $2, NOW())
`, site.ID, result.Up)
return err
}
Now we're ready to create our new CheckAll endpoint.
🥐 Create the new CheckAll endpoint inside monitor/check.go:
monitor/check.goimport "golang.org/x/sync/errgroup"
// CheckAll checks all sites.
//
//encore:api public method=POST path=/checkall
func CheckAll(ctx context.Context) error {
// Get all the tracked sites.
resp, err := site.List(ctx)
if err != nil {
return err
}
// Check up to 8 sites concurrently.
g, ctx := errgroup.WithContext(ctx)
g.SetLimit(8)
for _, site := range resp.Sites {
site := site // capture for closure
g.Go(func() error {
return check(ctx, site)
})
}
return g.Wait()
}
This uses an errgroup to check up to 8 sites concurrently, aborting early if we encounter any error. (Note that a website being down is not treated as an error.)
🥐 Run go get golang.org/x/sync/errgroup to install that dependency.
🥐 Now that we have a CheckAll endpoint, define a cron job to automatically call it every 1 hour (since this is an example, we don't need to go too crazy and check every minute):
monitor/check.goimport "encore.dev/cron"
// Check all tracked sites every 1 hour.
var _ = cron.NewJob("check-all", cron.JobConfig{
Title: "Check all sites",
Endpoint: CheckAll,
Every: 1 * cron.Hour,
})
Please note
Cron jobs are not triggered when running the application locally but work when deploying the application to a cloud environment.
The frontend needs a way to list all sites and display if they are up or down.
🥐 Add a file in the monitor service and name it status.go. Add the following code:
monitor/status.gopackage monitor
import (
"context"
"time"
)
// SiteStatus describes the current status of a site
// and when it was last checked.
type SiteStatus struct {
Up bool `json:"up"`
CheckedAt time.Time `json:"checked_at"`
}
// StatusResponse is the response type from the Status endpoint.
type StatusResponse struct {
// Sites contains the current status of all sites,
// keyed by the site ID.
Sites map[int]SiteStatus `json:"sites"`
}
// Status checks the current up/down status of all monitored sites.
//
//encore:api public method=GET path=/status
func Status(ctx context.Context) (*StatusResponse, error) {
rows, err := db.Query(ctx, `
SELECT DISTINCT ON (site_id) site_id, up, checked_at
FROM checks
ORDER BY site_id, checked_at DESC
`)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
defer rows.Close()
result := make(map[int]SiteStatus)
for rows.Next() {
var siteID int
var status SiteStatus
if err := rows.Scan(&siteID, &status.Up, &status.CheckedAt); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
result[siteID] = status
}
if err := rows.Err(); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
return &StatusResponse{Sites: result}, nil
}
Now try visiting http://localhost:4000/frontend in your browser again. This time you should see a working frontend that lists all sites and their current status.
5. Deploy
To try out your uptime monitor for real, let's deploy it to the cloud.
Encore supports building Docker images directly from the CLI, which can then be self-hosted on your own infrastructure of choice.
If your app is using infrastructure resources, such as SQL databases, Pub/Sub, or metrics, you will need to supply a runtime configuration your Docker image.
🥐 Create a new file infra-config.json in the root of your project with the following contents:
{
"$schema": "https://encore.dev/schemas/infra.schema.json",
"sql_servers": [
{
"host": "my-db-host:5432",
"databases": {
"monitor": {
"username": "my-db-owner",
"password": {"$env": "DB_PASSWORD"}
},
"site": {
"username": "my-db-owner",
"password": {"$env": "DB_PASSWORD"}
}
}
}
]
}
The values in this configuration are just examples, you will need to replace them with the correct values for your database.
🥐 Build a Docker image by running encore build docker uptime:v1.0.
This will compile your application using the host machine and then produce a Docker image containing the compiled application.
🥐 Upload the Docker image to the cloud provider of your choice and run it.
Encore Cloud provides automated infrastructure and DevOps. Deploy to a free development environment or to your own cloud account on AWS or GCP.
Create account
Before deploying with Encore Cloud, you need to have a free Encore Cloud account and link your app to the platform. If you already have an account, you can move on to the next step.
If you don’t have an account, the simplest way to get set up is by running encore app create and selecting Y when prompted to create a new account. Once your account is set up, continue creating a new app, selecting the empty app template.
After creating the app, copy your project files into the new app directory, ensuring that you do not replace the encore.app file (this file holds a unique id which links your app to the platform).
Commit changes
Encore comes with built-in CI/CD, and the deployment process is as simple as a git push.
(You can also integrate with GitHub to activate per Pull Request Preview Environments, learn more in the CI/CD docs.)
🥐 Now, let's deploy your app to Encore's free development cloud by running:
$ git add -A .$ git commit -m 'Initial commit'$ git push encoreEncore will now build and test your app, provision the needed infrastructure, and deploy your application to the cloud.
After triggering the deployment, you will see a URL where you can view its progress in the Encore Cloud dashboard. It will look something like: https://app.encore.cloud/$APP_ID/deploys/...
From the Cloud Dashboard you can also see metrics, trigger Cron Jobs, see traces, and later connect your own AWS or GCP account to use for deployment.
🥐 When the deploy has finished, you can try out your uptime monitor by going to https://staging-$APP_ID.encr.app/frontend.
You now have an Uptime Monitor running in the cloud, well done!
6. Publish Pub/Sub events when a site goes down
Hold on, an uptime monitoring system isn't very useful if it doesn't actually notify you when a site goes down.
To do so let's add a Pub/Sub topic on which we'll publish a message every time a site transitions from being up to being down, or vice versa.
🥐 Define the topic using Encore's Pub/Sub package in a new file, monitor/alerts.go:
monitor/alerts.gopackage monitor
import "encore.dev/pubsub"
// TransitionEvent describes a transition of a monitored site
// from up->down or from down->up.
type TransitionEvent struct {
// Site is the monitored site in question.
Site *site.Site `json:"site"`
// Up specifies whether the site is now up or down (the new value).
Up bool `json:"up"`
}
// TransitionTopic is a pubsub topic with transition events for when a monitored site
// transitions from up->down or from down->up.
var TransitionTopic = pubsub.NewTopic[*TransitionEvent]("uptime-transition", pubsub.TopicConfig{
DeliveryGuarantee: pubsub.AtLeastOnce,
})
Now let's publish a message on the TransitionTopic if a site's up/down
state differs from the previous measurement.
🥐 Create a getPreviousMeasurement function to report the last up/down state:
monitor/alerts.goimport (
"encore.dev/storage/sqldb"
"errors"
"context"
)
// getPreviousMeasurement reports whether the given site was
// up or down in the previous measurement.
func getPreviousMeasurement(ctx context.Context, siteID int) (up bool, err error) {
err = db.QueryRow(ctx, `
SELECT up FROM checks
WHERE site_id = $1
ORDER BY checked_at DESC
LIMIT 1
`, siteID).Scan(&up)
if errors.Is(err, sqldb.ErrNoRows) {
// There was no previous ping; treat this as if the site was up before
return true, nil
} else if err != nil {
return false, err
}
return up, nil
}
🥐 Now add a function to conditionally publish a message if the up/down state differs:
monitor/alerts.goimport "encore.app/site"
func publishOnTransition(ctx context.Context, site *site.Site, isUp bool) error {
wasUp, err := getPreviousMeasurement(ctx, site.ID)
if err != nil {
return err
}
if isUp == wasUp {
// Nothing to do
return nil
}
_, err = TransitionTopic.Publish(ctx, &TransitionEvent{
Site: site,
Up: isUp,
})
return err
}
🥐 Finally modify the check function to call this function:
monitor/check.gofunc check(ctx context.Context, site *site.Site) error {
result, err := Ping(ctx, site.URL)
if err != nil {
return err
}
// Publish a Pub/Sub message if the site transitions
// from up->down or from down->up.
if err := publishOnTransition(ctx, site, result.Up); err != nil {
return err
}
_, err = db.Exec(ctx, `
INSERT INTO checks (site_id, up, checked_at)
VALUES ($1, $2, NOW())
`, site.ID, result.Up)
return err
}
Now the monitoring system will publish messages on the TransitionTopic
whenever a monitored site transitions from up->down or from down->up.
It doesn't know or care who actually listens to these messages.
The truth is right now nobody does. So let's fix that by adding a Pub/Sub subscriber that posts these events to Slack.
7. Send Slack notifications when a site goes down
🥐 Start by creating a Slack service containing the following:
slack/slack.gopackage slack
import (
"bytes"
"context"
"encoding/json"
"fmt"
"io"
"net/http"
)
type NotifyParams struct {
// Text is the Slack message text to send.
Text string `json:"text"`
}
// Notify sends a Slack message to a pre-configured channel using a
// Slack Incoming Webhook (see https://api.slack.com/messaging/webhooks).
//
//encore:api private
func Notify(ctx context.Context, p *NotifyParams) error {
reqBody, err := json.Marshal(p)
if err != nil {
return err
}
req, err := http.NewRequestWithContext(ctx, "POST", secrets.SlackWebhookURL, bytes.NewReader(reqBody))
if err != nil {
return err
}
resp, err := http.DefaultClient.Do(req)
if err != nil {
return err
}
defer resp.Body.Close()
if resp.StatusCode >= 400 {
body, _ := io.ReadAll(resp.Body)
return fmt.Errorf("notify slack: %s: %s", resp.Status, body)
}
return nil
}
var secrets struct {
// SlackWebhookURL defines the Slack webhook URL to send
// uptime notifications to.
SlackWebhookURL string
}
🥐 Now go to a Slack community of your choice where you have the permission to create a new Incoming Webhook.
🥐 Once you have the Webhook URL, set it as an Encore secret:
$ encore secret set --type dev,local,pr SlackWebhookURLEnter secret value: *****Successfully updated development secret SlackWebhookURL.🥐 Test the slack.Notify endpoint by calling it via cURL:
$ curl 'http://localhost:4000/slack.Notify' -d '{"Text": "Testing Slack webhook"}'You should see the Testing Slack webhook message appear in the Slack channel you designated for the webhook.
🥐 When it works it's time to add a Pub/Sub subscriber to automatically notify Slack when a monitored site goes up or down. Add the following:
slack/slack.goimport (
"encore.dev/pubsub"
"encore.app/monitor"
)
var _ = pubsub.NewSubscription(monitor.TransitionTopic, "slack-notification", pubsub.SubscriptionConfig[*monitor.TransitionEvent]{
Handler: func(ctx context.Context, event *monitor.TransitionEvent) error {
// Compose our message.
msg := fmt.Sprintf("*%s is down!*", event.Site.URL)
if event.Up {
msg = fmt.Sprintf("*%s is back up.*", event.Site.URL)
}
// Send the Slack notification.
return Notify(ctx, &NotifyParams{Text: msg})
},
})
8. Deploy your finished Uptime Monitor
Now you're ready to deploy your finished Uptime Monitor, complete with a Slack integration.
Because we have added more infrastructure to our app, we need to update the configuration in our infra-config.json to include the new Pub/Sub topic and subscription as well as how we should set the SlackWebhookURL secret.
🥐 Update your ìnfra-config.json to reflect the new infrastructure.
🥐 Build a Docker image by running encore build docker uptime:v2.0.
🥐 Upload the Docker image to the cloud provider and run it.
🥐 As before, deploying your app to the cloud is as simple as running:
$ git add -A .$ git commit -m 'Add slack integration'$ git push encoreCelebrate with fireworks
Now that your app is running in the cloud, let's celebrate with some fireworks:
🥐 In the Cloud Dashboard, open the Command Menu by pressing Cmd + K (Mac) or Ctrl + K (Windows/Linux).
From here you can easily access all Cloud Dashboard features and for example jump straight to specific services in the Service Catalog or view Traces for specific endpoints.
🥐 Type fireworks in the Command Menu and press enter. Sit back and enjoy the show!
Conclusion
We've now built a fully functioning uptime monitoring system.
If we may say so ourselves (and we may; it's our documentation after all) it's pretty remarkable how much we've accomplished in such little code:
- We've built three different services (
site,monitor, andslack) - We've added two databases (to the
siteandmonitorservices) for tracking monitored sites and the monitoring results - We've added a cron job for automatically checking the sites every hour
- We've set up a Pub/Sub topic to decouple the monitoring system from the Slack notifications
- We've added a Slack integration, using secrets to securely store the webhook URL, listening to a Pub/Sub subscription for up/down transition events
All of this in just a bit over 300 lines of code. It's time to lean back and take a sip of your favorite beverage, safe in the knowledge you'll never be caught unaware of a website going down suddenly.